Artificial Intelligence
AI, or Artificial Intelligence, refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. It involves the development of algorithms and models that enable computers to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include problem-solving, speech recognition, learning, perception, and language translation.
There are two main types of AI: Narrow AI (or Weak AI) and General AI (or Strong AI). Narrow AI is designed for a specific task, while General AI is more versatile and capable of performing any intellectual task that a human being can.
AI applications are diverse and can be found in areas such as natural language processing, image and speech recognition, autonomous vehicles, healthcare, finance, and many more. Machine learning, a subset of AI, involves training models with data to improve their performance over time without explicit programming.
Artificial Intelligence encompasses computer systems capable of performing tasks requiring human-like intelligence. Key AI technologies include symbolic reasoning, machine learning (supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning), deep learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics. AI's future resembles the early stages of the internet, with exponential growth expected, leading to transformative impacts across various fields. While concerns about job displacement exist, embracing AI and acquiring relevant skills can amplify productivity and mitigate the risk of replacement.
Artificial Intelligence aims to create systems that emulate human intelligence. It encompasses various fields such as speech recognition, natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, robotics, pattern recognition, machine learning, and deep learning. These fields utilize techniques like neural networks, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) to replicate human cognitive abilities. Machine learning involves feeding machines large datasets to enable pattern recognition and prediction, with approaches including supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. AI applications range from classification to prediction, with algorithms trained through trial-and-error to achieve goals in reinforcement learning.
Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
AI is increasingly being integrated into various aspects of healthcare, bringing about improvements in diagnostics, treatment planning, patient care, and administrative tasks. Here are some examples of how AI is used in healthcare:
Diagnostic Imaging
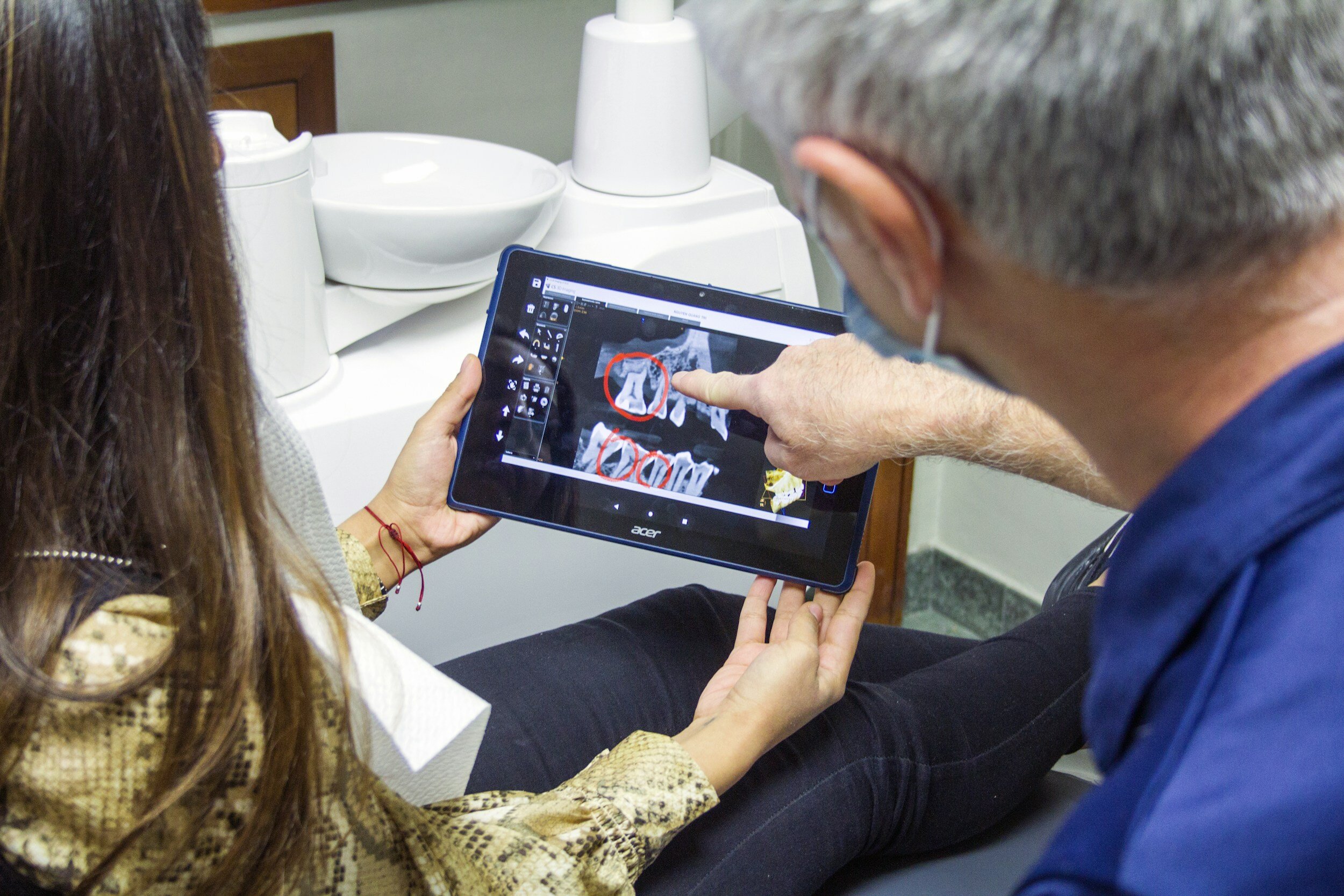
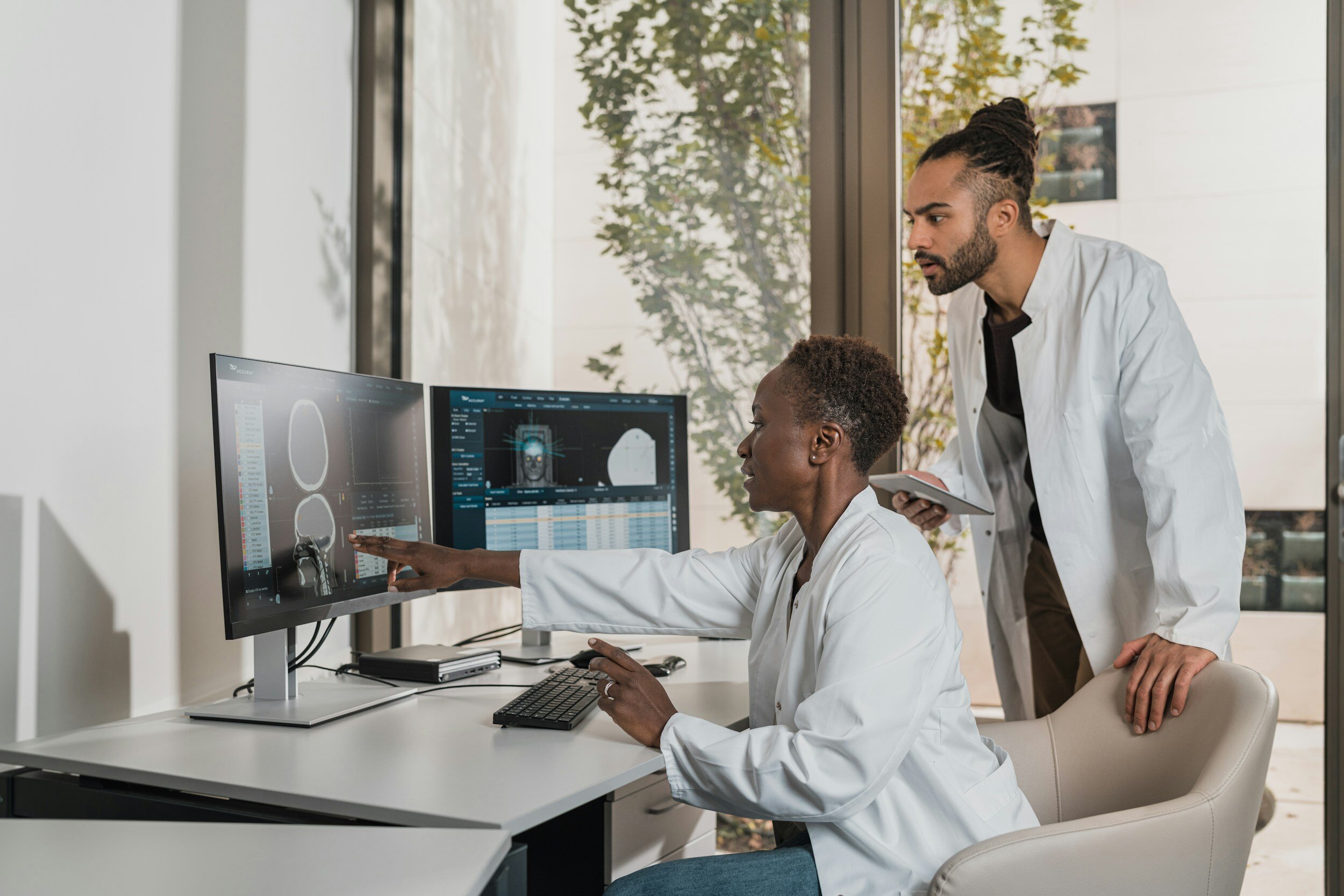
AI is used to analyze medical images, such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, to detect abnormalities and assist radiologists in making more accurate diagnoses. This can speed up the diagnostic process and improve the early detection of diseases.
Predictive Analytics
AI algorithms analyze patient data to identify patterns and predict potential health issues. This helps healthcare providers intervene early, manage chronic conditions, and personalize treatment plans.
Drug Discovery
AI is used in pharmaceutical research to analyze vast datasets and identify potential drug candidates more efficiently. It accelerates the drug discovery process by predicting how molecules will behave and their potential effectiveness.
Personalized Medicine
AI helps analyze genetic and molecular data to tailor treatments based on individual patient profiles. This can lead to more effective and targeted therapies with fewer side effects.
Virtual Health Assistants
Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by AI are used to provide information, answer queries, and offer basic healthcare advice. They can also schedule appointments and remind patients to take medications.
Robot-Assisted Surgery
AI is integrated into robotic surgical systems to enhance precision and control during surgery. Surgeons can benefit from real-time data analysis and assistance, leading to better outcomes.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP is employed for extracting valuable information from clinical notes, medical records, and research articles. This helps in data mining, improving documentation, and aiding in clinical decision-making.
Remote Patient Monitoring
AI enables continuous monitoring of patients outside traditional healthcare settings. Wearable devices and sensors collect data, providing healthcare professionals with real-time information on patients' vital signs and overall health.
Fraud Detection and Billing
AI algorithms are used to detect fraudulent activities in healthcare billing, ensuring that insurance claims are accurate and reducing instances of fraud.
Administrative Tasks
AI is applied to automate administrative tasks such as appointment scheduling, billing, and coding. This helps in streamlining healthcare operations and reducing administrative burdens on healthcare professionals.